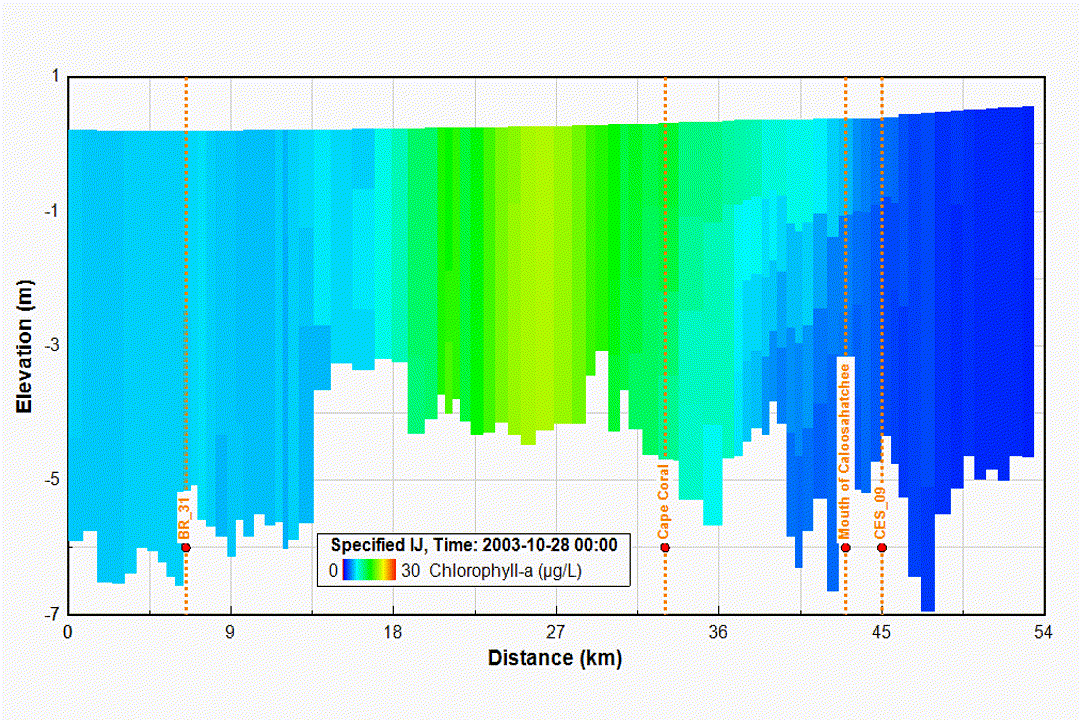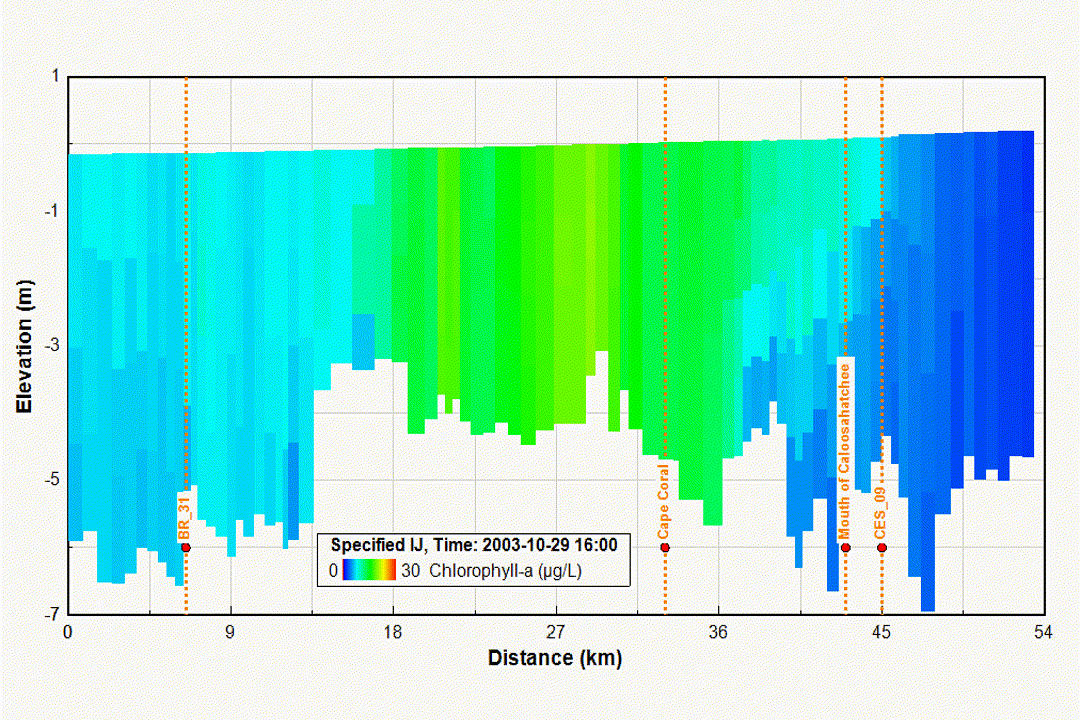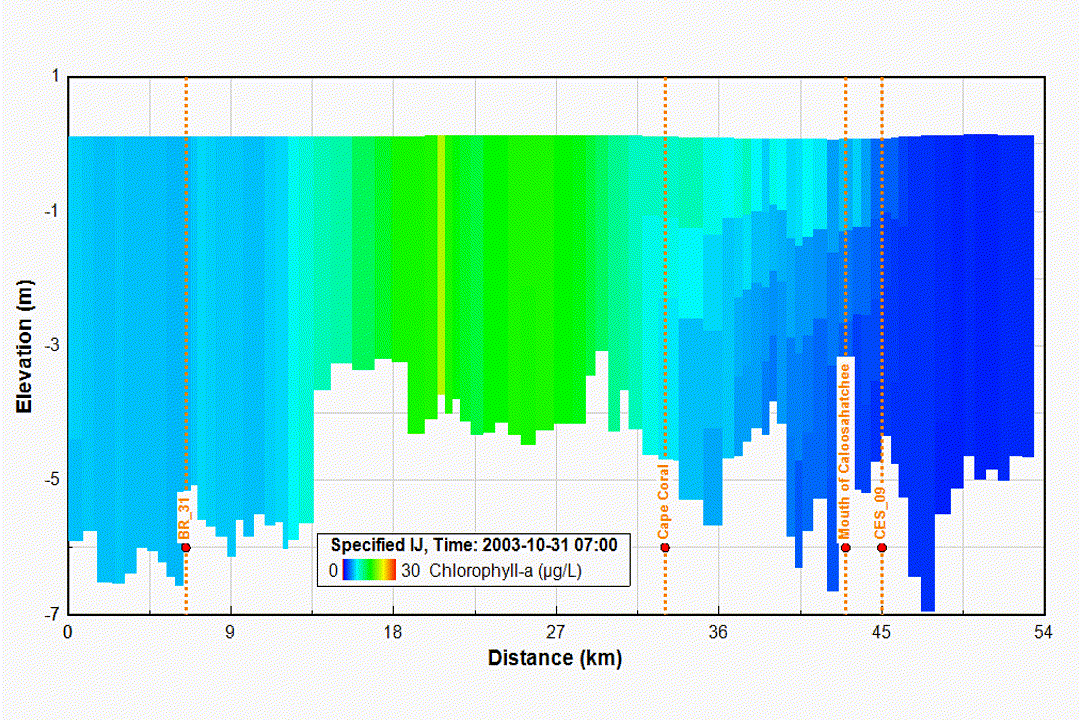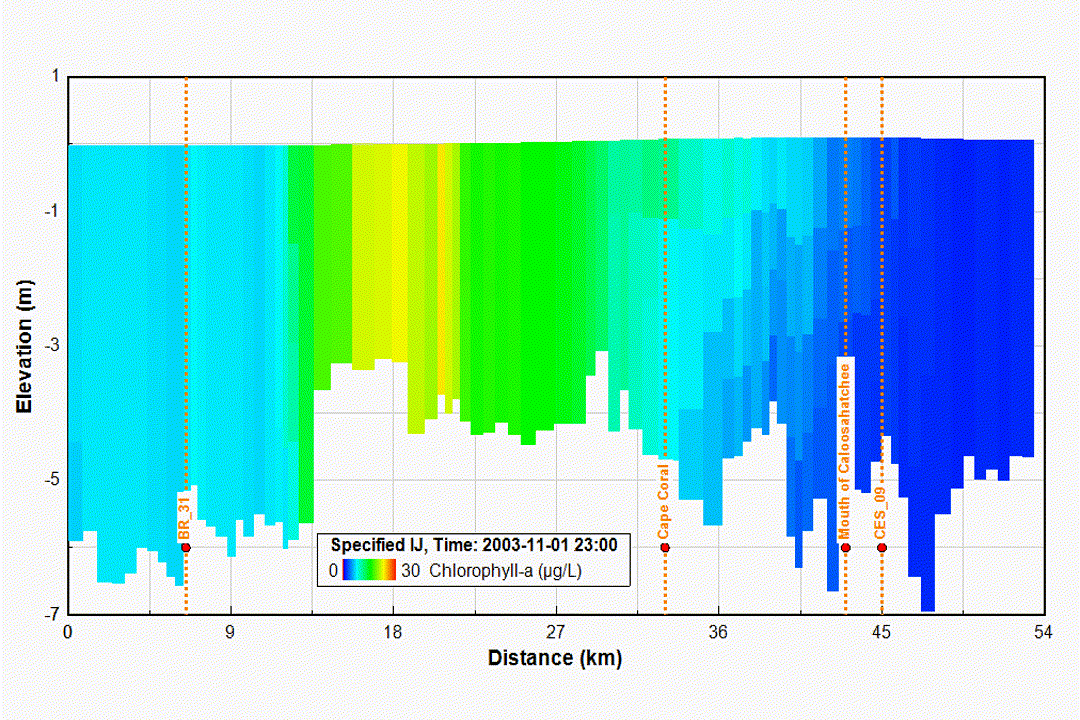
Eutrophication and Water Quality
Human activities increase the level of nutrients in surface water bodies, leading to severe algal blooms, lowering dissolved oxygen, and often killing fish and other organisms. To better understand the impacts of numerous factors on your ecosystem and support informed decisions for mitigation, EFDC+ provides you a range of tools from simple to complex, all in one coupled model.
Full Eutrophication Module
EFDC+ includes a complete eutrophication water quality module with unlimited phytoplankton and zooplankton groups, allowing you enormous flexibility and control. The model simulates spatial and temporal distributions of water quality parameters, including dissolved oxygen, suspended algae, various components of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and silica cycles, waterborne bacteria, and rooted plants.
Unlimited Algal Groups
The EFDC+ eutrophication module has been refactored and enhanced to allow for the definition of a general phytoplankton group. Based on their conceptual model of the aquatic ecosystem, users will now be able to simulate an unlimited number of algal and periphyton groups. Each group assigned different settling, half-saturation constants, uptake rates for nutrients, etc.
Unlimited Zooplankton Groups
Zooplankton plays a significant role in water body nutrient dynamics as grazers controlling algal and bacterial populations. Therefore, a module for zooplankton kinetics has been implemented in EDFC+ version 10.3, based primarily on the formulation provided in Cerco and Noel (2004). The model defines a general group to simulate an unlimited number of zooplankton groups.
Sediment Diagenesis
To enhance a model’s predictive capability of water quality parameters, as well as simulate long-term changes in water quality conditions in response to changes in nutrient loadings, EFDC+ has coupled the sediment process model with the water quality model. The enhanced EFDC+ sediment diagenesis module was originally developed for the Chesapeake Bay Model by DiToro, which simulates twenty-seven state variables. This module predicts the flux of nutrients between the sediment and the water column.
Aquatic Vegetation
The Rooted Plant and Epiphyte Module (RPEM) in EFDC+ simulates submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV), commonly observed along the banks of many rivers and lakes. In this module, you have the option to link the water and sediment nutrients to the growth and decay of aquatic vegetation. In addition to simulating SAV, this module allows for representative simulation of epiphytes growing on the plants, which is critical for accurately evaluating nutrient uptake in wetlands.